JavaScript
JavaScript
JavaScript is a high-level, object-oriented, multi-paradigm programming language.
Chapter 1
1. Values and variables
Values: Smallest unit in JS, store them in variables. let firstName = JonasfirstName is a box irl, Jonas is the value in the box. camelCase 驼峰命名 第一个单词小写,后面的首字母大写
2. Senven primitive data type in JavaScript
- Number: Floating point numbers, used for decimals and integers
let age = 23; - String: Sequence of characters, used for text
- Boolean: Logical type that only can be
trueorfalse, used for taking decision - Undefined: Value taken by a variable that is not yet defined
let age; - Null: Also means empty value
- Symbol(ES2015): Value that is unique and cannot be changed [Not useful for now]
- BigInt(ES2020): Larger integers than the Number type can hold
Dynamic Typing: JavaScript can automatically determine the datatype of the value.
3. let, const, var
let: define mutable variable const: define immutable variable (constant, no const age; ) var: function scope
4. Operators
- math: +, -, *, /
- assignment: +=, -=, ++, --, =
x++; //x=x+1 - comparison: >, <, <=, >=, ==
- logic
4.1 Precedence
()优先级最高
5. Templates Literals 模板文字
const jonasNew = `I'm ${firstName}, a ${year - birthYear} year old ${job}!`;
console.log(jonasNew);//这两段输出一样 用反引号可以快速实现多行文字输出
console.log(
'String with \n\
multiple \n\
lines'
);
console.log(`String
multiple
lines`);6. If_else
7. Type Conversion and Coercion
Number('32') --> 32+ 运算符强制转换所有为字符串 2+3+4+'5' 输出为'95'- 运算符强制转换所有为数字
8. Truthy and Falsy Values
5 falsy values: 0, '', undefined, Null, NaN (Not a Number) Boolean(0) 会变成false
const money = 100;$$
if (money) {
console.log("Don't spend it all ;)");
} else {
console.log('You should get a job!');
}
输出为'You should get a job!',因为if else 会自动执行boolean化9. ==vs===
lose strict == will perform type coercion '18'==18 True'18'===18 Falseprompt('What's your favorate number?')
10. Statements and Expressions (声明和表达式)
Expressions: 3+4 能产生一个 value Statements 不能
11. ECMAScript 2015 / ES6 / ES2015
Huge change. 向后兼容性
Hints
- 把脚本置于
<body>元素的底部,可改善显示速度,因为脚本编译会拖慢显示。 - 更改 HTML 元素的 innerHTML 属性是在 HTML 中显示数据的常用方法。
- 在 HTML 文档完全加载后使用 document.write() 将删除所有已有的 HTML。
- 在 HTML 中,JavaScript 程序由 web 浏览器执行。
- JavaScript 语句由以下构成:值、运算符、表达式、关键词和注释。
- JavaScript 拥有空白折叠。
- JavaScript 语句常常通过某个关键词来标识需要执行的 JavaScript 动作。
| 关键词 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| break | 终止 switch 或循环 |
| continue | 跳出循环并在顶端开始 |
| debugger | 停止执行 JavaScript,并调用调试函数(如果可用) |
| do ... while | 执行语句块,并在条件为真时重复代码块 |
| for | 标记需被执行的语句块,只要条件为真 |
| function | 声明函数 |
| if ... else | 标记需被执行的语句块,根据某个条件 |
| return | 退出函数 |
| switch | 标记需被执行的语句块,根据不同的情况 |
| try ... catch | 对语句块实现错误处理 |
| var | 声明变量 |
- 所有 JavaScript 标识符对大小写敏感。变量 lastName 和 lastname,是两个不同的变量。
- JavaScript 程序员倾向于使用以小写字母开头的驼峰大小写
- ES2015 引入了两个重要的 JavaScript 新关键词:
let和const。这两个关键字在 JavaScript 中提供了块作用域(Block Scope)变量(和常量)。在 ES2015 之前,JavaScript 只有两种类型的作用域:全局作用域和函数作用域。 - 局部变量只能在它们被声明的函数内访问(函数作用域)。
// 此处的代码不可以使用 carName
function myFunction() {
var carName = 'porsche';
// code here CAN use carName
}
// 此处的代码不可以使用 carName- 块作用域 可以使用 let 关键词声明拥有块作用域的变量。 在块 {} 内声明的变量无法从块外访问:
{
let x = 10;
}
// 此处不可以使用 x通过 var 关键词声明的变量没有块作用域。在块 {} 内声明的变量可以从块之外进行访问。
- 使用 var 关键字重新声明变量会带来问题,在块中重新声明变量也将重新声明块外的变量。 使用 let 关键字重新声明变量可以解决这个问题,在块中重新声明变量不会重新声明块外的变量。
var x = 10;
// 此处 x 为 10
{
let x = 6;
// 此处 x 为 6
}
// 此处 x 为 10循环作用域 在循环中使用的变量使用 var 会重新声明循环之外的变量。(for var i=... 会改变原来的 var) 在循环中使用的变量使用 let 并没有重新声明循环外的变量。 如果在循环中用 let 声明了变量 i,那么只有在循环内,变量 i 才是可见的。
在 HTML 中,通过 var 定义的全局变量会成为 window 变量。通过 let 关键词定义的全局变量不属于 window 对象,不可以使用 windows.nameTest()
允许在程序的任何位置使用 var 重新声明 JavaScript 变量 在相同的作用域,或在相同的块中,通过 let 重新声明一个 var 变量是不允许的 在相同的作用域,或在相同的块中,通过 let 重新声明一个 let 变量是不允许的 在相同的作用域,或在相同的块中,通过 var 重新声明一个 let 变量是不允许的 在不同的作用域或块中,通过 let 重新声明变量是允许的:
通过 var 声明的变量会提升到顶端。
// 在此处,您可以使用 carName
var carName;- 可以更改常量对象的属性,可以更改常量数组的元素。
- 位运算符
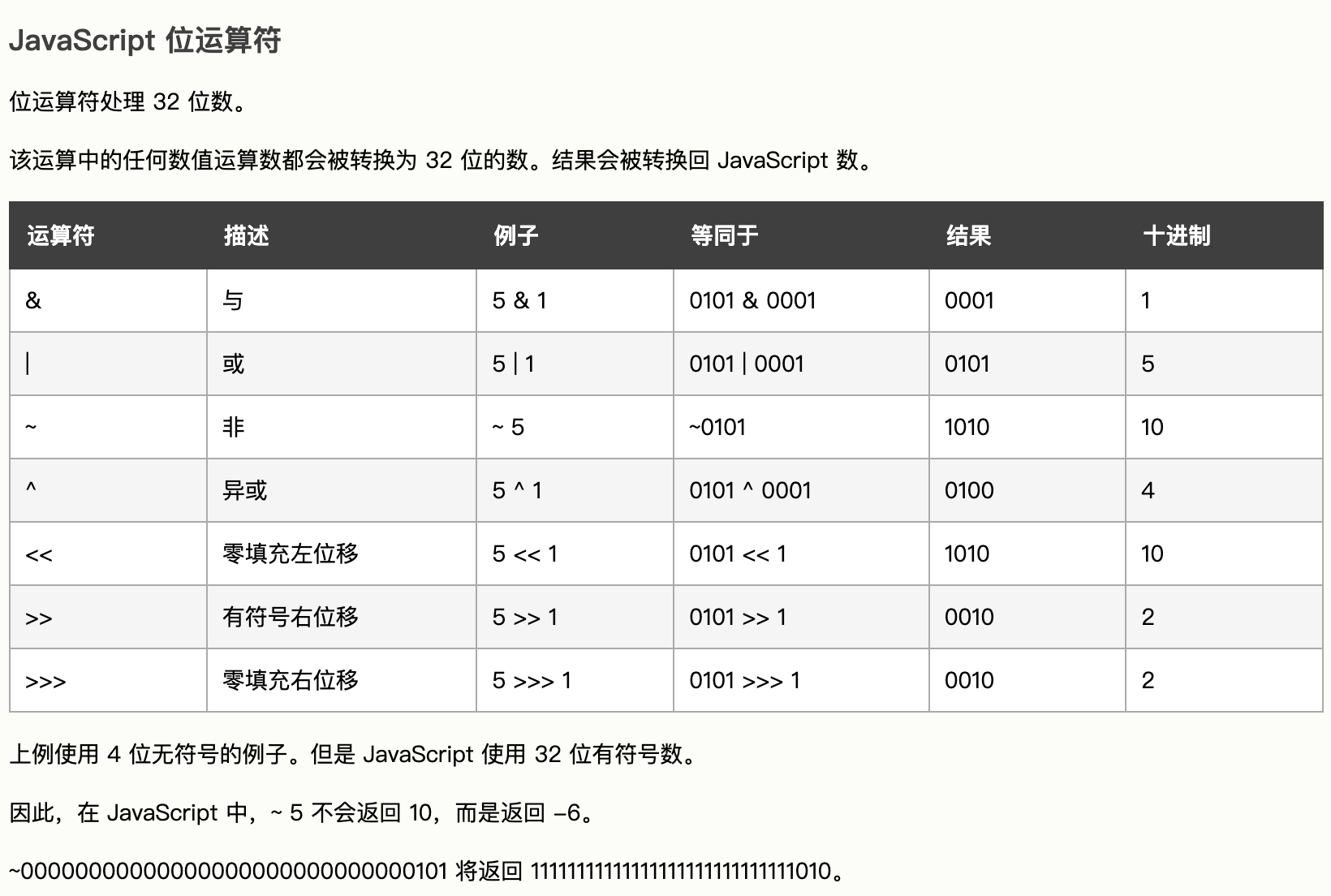
- 在 JavaScript 中,null 的数据类型是对象。
- Null 和 undefined
typeof undefined; // undefined
typeof null; // object
null === undefined; // false
null == undefined; // true- 当 JavaScript 到达 return 语句,函数将停止执行。
- 不使用 () 访问函数将返回函数声明而不是函数结果。
- 如果通过关键词 "new" 来声明 JavaScript 变量,则该变量会被创建为对象。避免字符串、数值或逻辑对象。他们会增加代码的复杂性并降低执行速度。
- replace() 只替换首个匹配,区分大小写。
Chapter 2
1. Strict Mode 严格模式
'use strict mode' at the first line of the JS file.
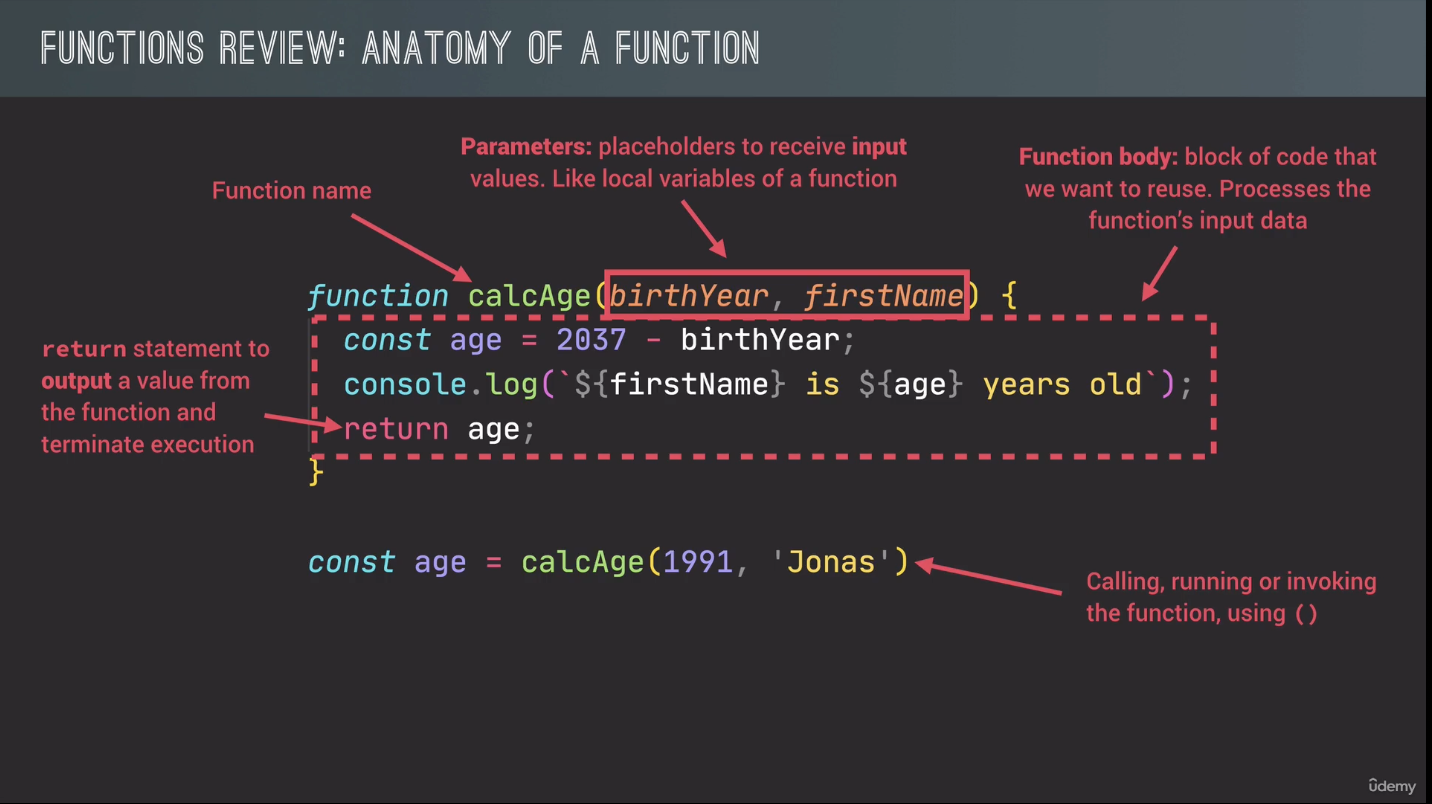
2. Function 函数
函数就是一个值
function logger() {
// function body
}
logger(); // invoking the function 调用函数
//
// Function declaration 可以在声明前就调用函数(Hoisting 提升)
function calcAge1(birthYeah) {
return 2037 - birthYeah;
}
const age1 = calcAge1(1991);
// Function expression
const calcAge2 = function (birthYeah) {
return 2037 - birthYeah;
};
const age2 = calcAge2(1991);
console.log(age1, age2);2.1 Function Declaration and Function Expression 函数声明和函数表达式
// Function declaration 可以在声明前就调用函数(Hoisting 提升)
function calcAge1(birthYeah) {
return 2037 - birthYeah;
}
const age1 = calcAge1(1991);
// Function expression
const calcAge2 = function (birthYeah) {
return 2037 - birthYeah;
};
const age2 = calcAge2(1991);
console.log(age1, age2);2.2 Arrow Function 箭头函数
ES6 添加到 Javascript
const yearsUntilRetirement = (birthYeah, firstName) => {
const age = 2037 - birthYeah;
const retirement = 65 - age;
// return retirement;
return `${firstName} retires in ${retirement} years`;
};
console.log(yearsUntilRetirement(1991, 'Jonas'));
console.log(yearsUntilRetirement(1980, 'Bob'));Ruturn 在返回值后会立刻退出函数,接下来的语句不会再执行。
3. Arrays
push 添加元素在数组末尾 unshift 添加元素在数组开头 数组的 push 会返回添加前数组的长度 unshift 也会 pop 删除在数组末尾的元素 shift 删除在数组开头的元素 indexOf 返回元素在数组的索引 includes 元素在数组中则返回 true
4. Objects
Order doesn't matter at all.
// 创建对象
const jonas = {
firstName: 'Jonas',
lastName: 'Schmedtmann',
age: 2037 - 1991,
job: 'teacher',
friends: ['Michael', 'Peter', 'Steven'],
};
// 需要先计算属性名时,用括号表示。 其余都可以直接使用点属性表示。
console.log(jonas.lastName);
console.log(jonas['lastName']);
// 不可以直接将变量名作为属性名,这个时候需要用括号表示。d
const intersted = prompt('What do you want to know about Jonas?');
console.log(jonas.intersted);
console.log(jonas[intersted]);
// 添加属性
jonas.location = 'Portugal';
jonas['twitter'] = '@jonasschmedtman';
console.log(jonas);5. Loops
5.1 For Loops
for loops keep running while condition is TRUE.
5.2 While Loops
breakwhile(1)
Chapter 3
1. DOM Manipulation 操作
Document Object Model -- Web APIs
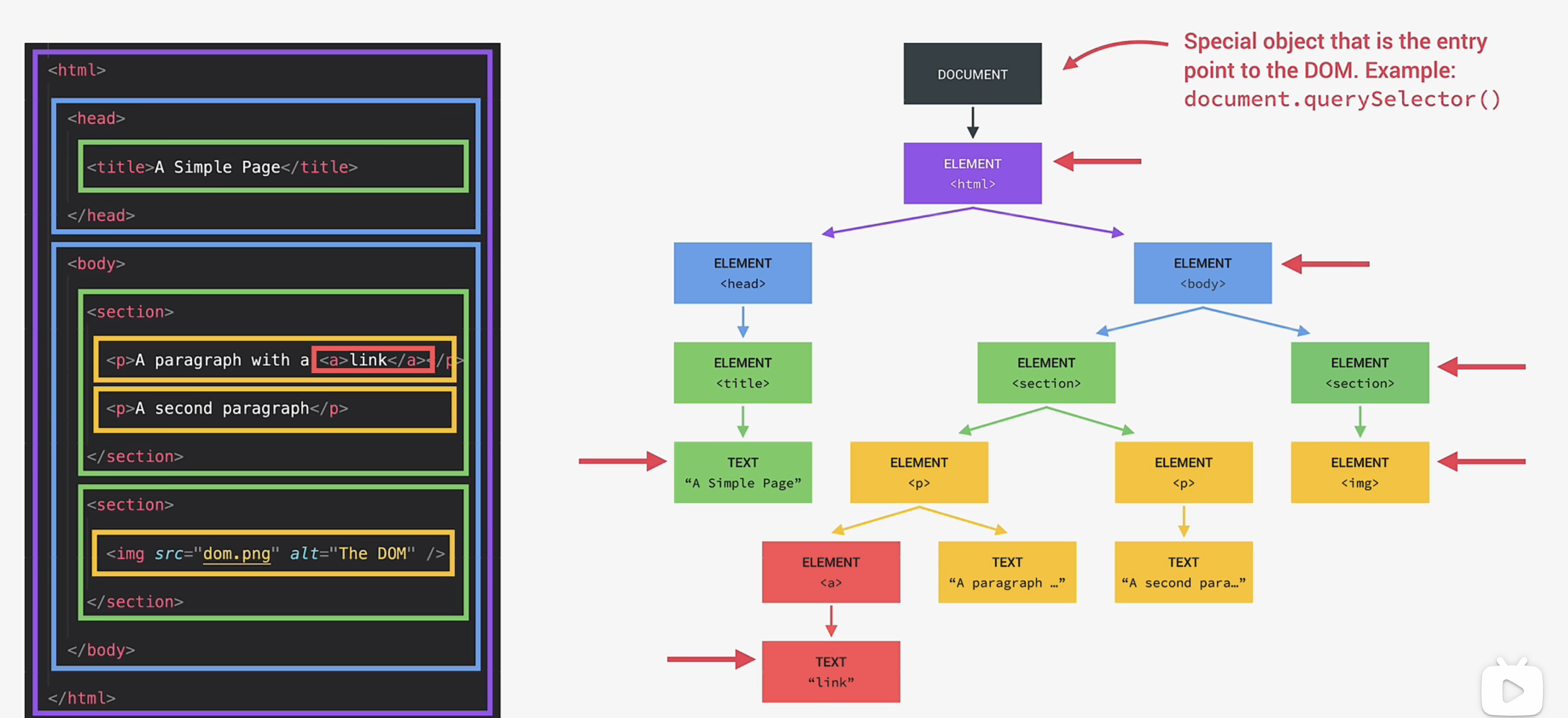 Whatever is in the HTML document also has to be in the DOM. The DOM is the complete representation of the HTML document, so that we can manipulate it in complex ways.
Whatever is in the HTML document also has to be in the DOM. The DOM is the complete representation of the HTML document, so that we can manipulate it in complex ways. modal.classList.remove('hidden');document.getElementById()document.querySelector()
Chapter 4
1. JS 的特点
- High-level
- Garbage-collected
- Interpreted / just-in-time compiled 解释型/实时编译型
- Prototyp-based object-oriented
- First-class functions
- Dynamic
- Single-threaded
- Non-blocking event loop
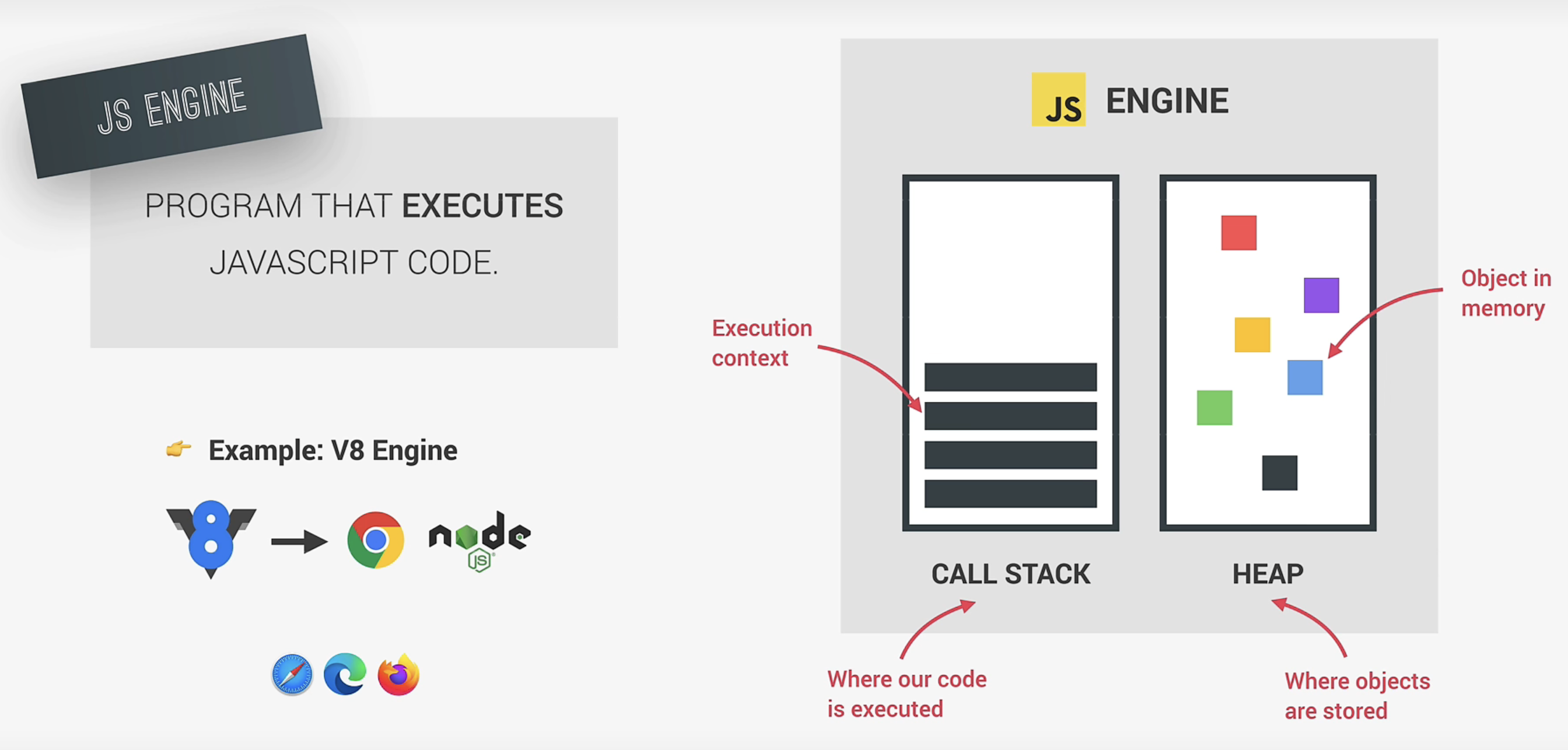
2. Javascript Engine
Call stack and Heap 调用栈:代码实际执行的地方,using Execution Contexts(执行上下文) 堆:一个非结构化的内存池,储存了我们的应用程序需要的所有对象。
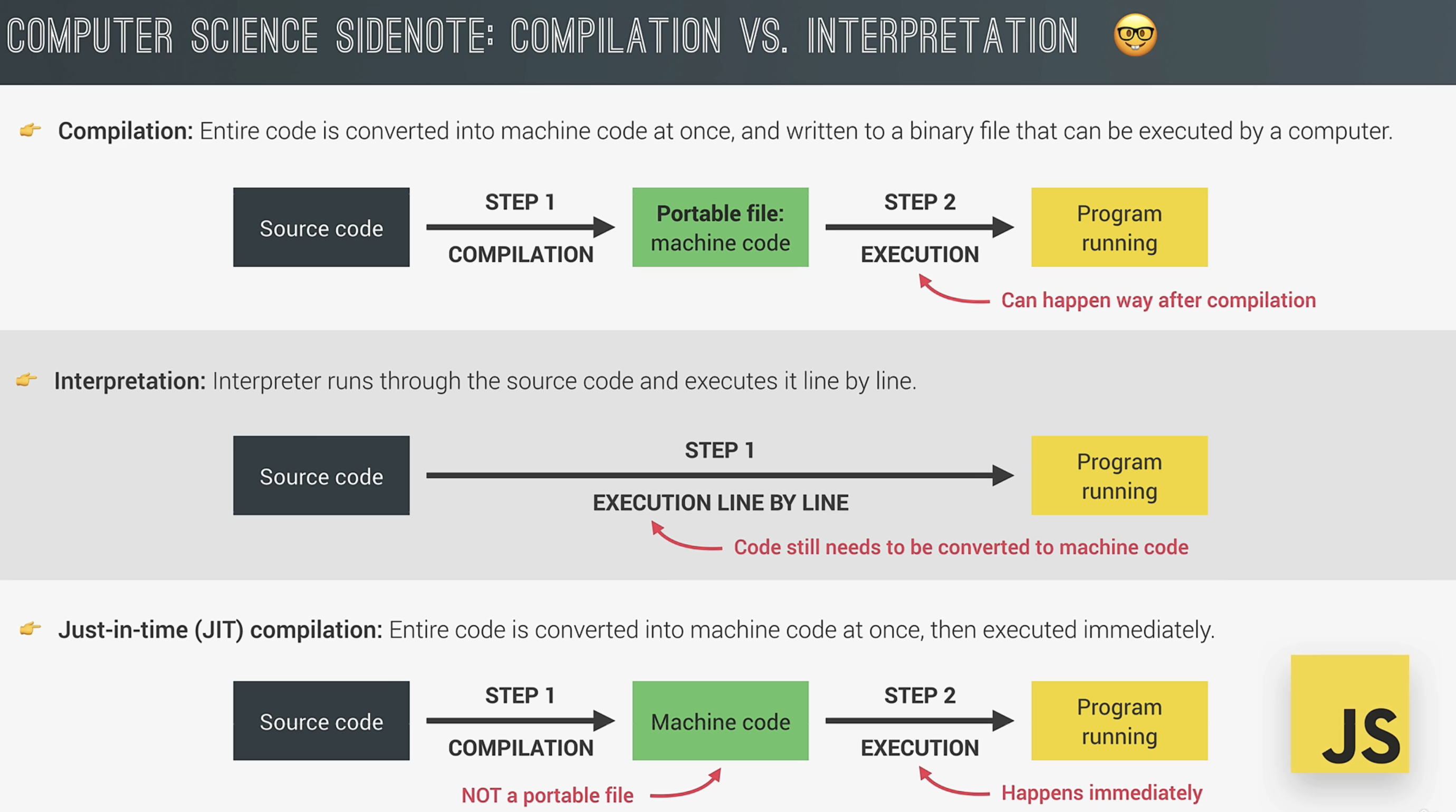
3. Execution Contexts 执行上下文:
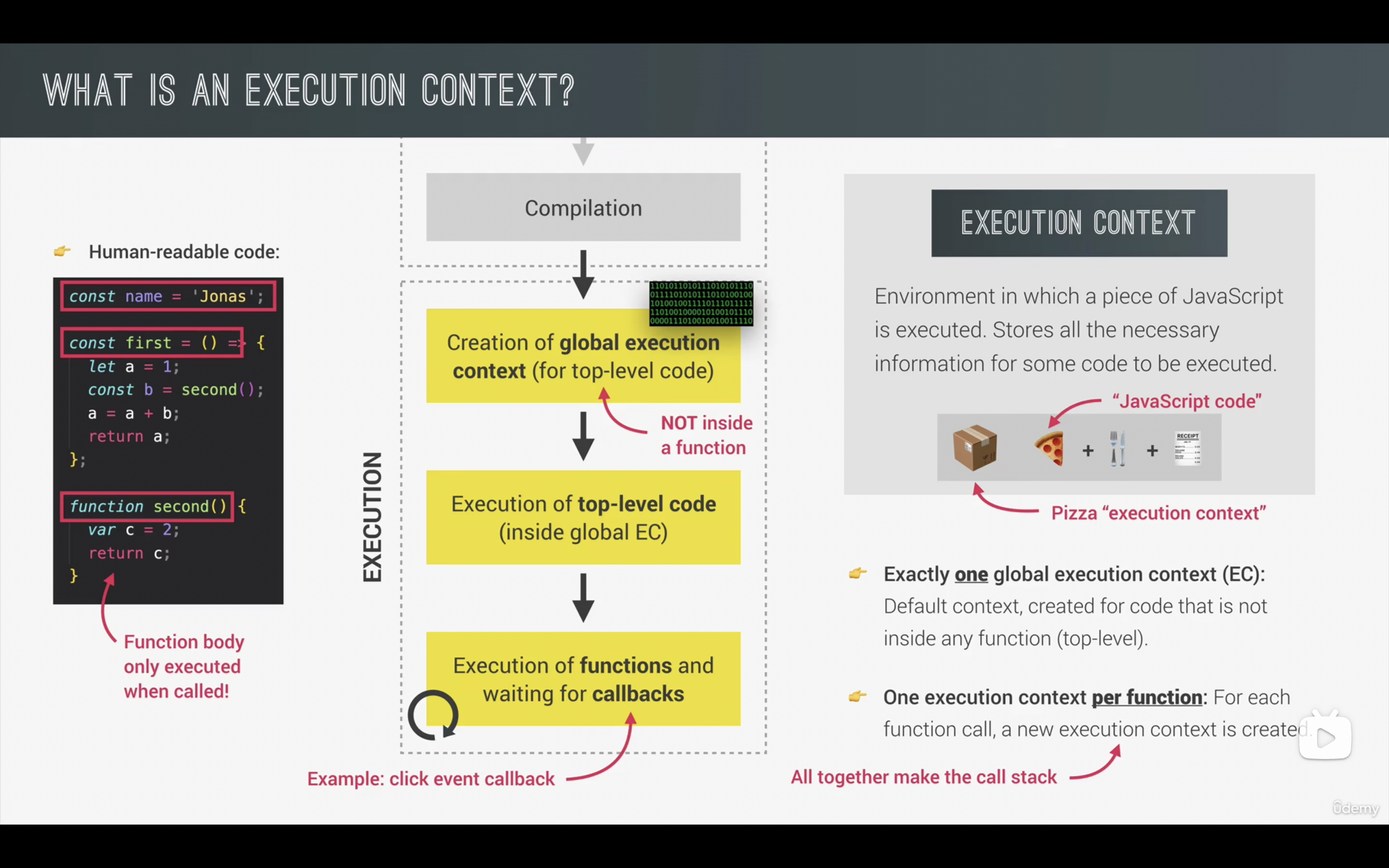 每次当控制器转到可执行代码的时候,就会进入一个执行上下文。执行上下文可以理解为当前代码的执行环境,它会形成一个作用域。JavaScript 中的运行环境大概包括三种情况。
每次当控制器转到可执行代码的时候,就会进入一个执行上下文。执行上下文可以理解为当前代码的执行环境,它会形成一个作用域。JavaScript 中的运行环境大概包括三种情况。
- 全局环境:JavaScript 代码运行起来会首先进入该环境
- 函数环境:当函数被调用执行时,会进入当前函数中执行代码
- eval(不建议使用,可忽略) 因此在一个 JavaScript 程序中,必定会产生多个执行上下文,JavaScript 引擎会以栈的方式来处理它们,这个栈,我们称其为函数调用栈(call stack)。栈底永远都是全局上下文,而栈顶就是当前正在执行的上下文。https://www.jianshu.com/p/a6d37c77e8db
3.1 What's inside Execution Contexts?
- Variable Environment 变量环境
- Scope chain 作用域链
- this Keyword 全局执行上下文 Global execution contexts 首先被创建(所有函数以外的代码),然后进入调用栈 Call stack,调用函数后,global 暂停运行,创建函数的执行上下文入栈,位于栈顶。JS 引擎首先执行栈顶的代码,出栈后再继续执行下面的,因为 JS 是单线程。
3.2 Scope chain
Global scope 全局作用域
Function scope 函数作用域
Block scope (ES6) 块作用域 花括号里的 只有 let const 有效 var 仍然可以在外面访问
 变量查找 variable lookup 只能查找父作用域 形成作用域链。 作用域链:查找一个变量时先在自己本身作用域中找,当自身作用域中没有时就会一层一层向外找
变量查找 variable lookup 只能查找父作用域 形成作用域链。 作用域链:查找一个变量时先在自己本身作用域中找,当自身作用域中没有时就会一层一层向外找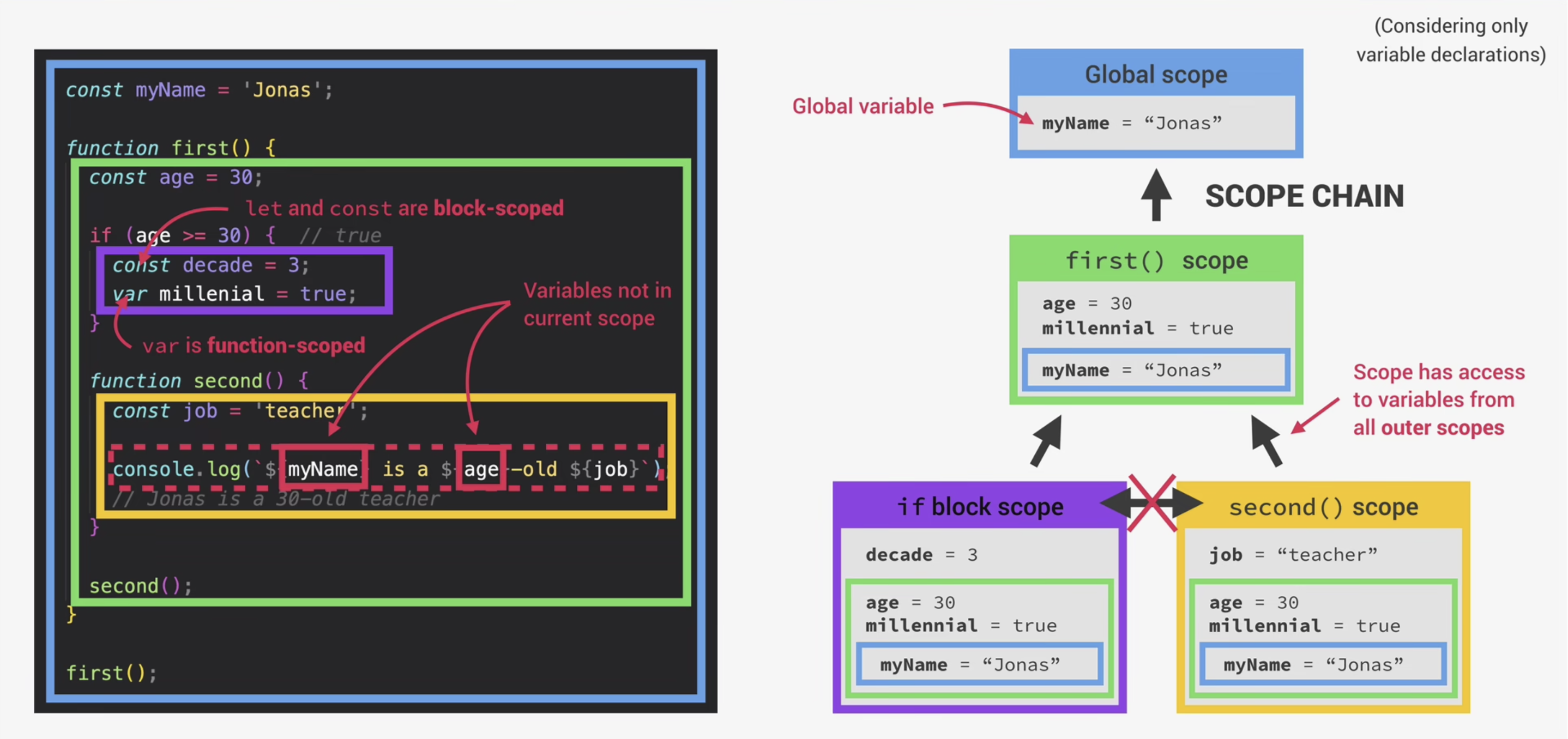
4. Hoisting 提升
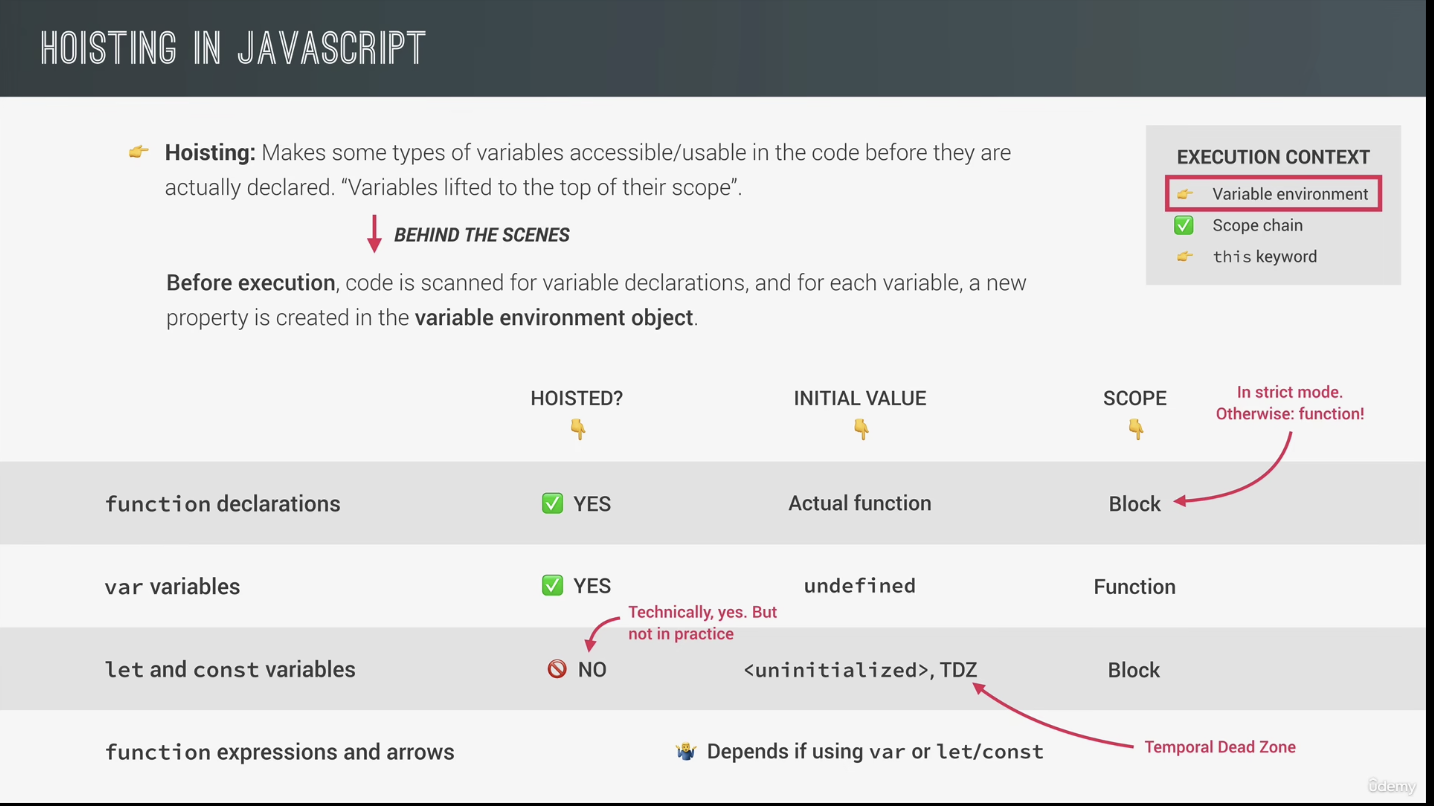
4.1 Temporal Dead Zone(TDZ) 临时死区
let 和 const 声明的变量不会被提升到作用域顶部,如果在声明前访问这些变量,会导致错误。 这是因为 JavaScript 引擎在扫描代码发现变量声明时,要么将他们提升到作用域顶部(遇到 var 声明),要么将声明放在 TDZ 中(遇到 let 和 const 声明)。访问 TDZ 中的变量会触发运行时错误。只有执行过变量声明语句后,变量才会从 TDZ 中移除,然后方可访问。
5. this keyword

this表示当前对象的一个引用。 this的指向:this 不是固定不变的,是根据调用的上下文(执行时环境)改变而改变。 如果单独使用,this 表示全局对象。 在方法中,this 表示该方法所属的对象。 在函数中,this 表示全局对象。 在函数中,在严格模式下,this 是未定义的(undefined),不然也是全局对象 windows。 在事件中,this 表示接收事件的元素。(Event listener)
5.1 this 的指向
5.1.1 全局环境
全局环境就是在<script></script>里面,这里的 this 始终指向的是 window 对象。
<script>console.log(this); // 全局环境,即window对象下,this -> window</script>5.1.2 局部环境
严格模式下,函数中的 this 为 undefined; 1)在全局作用域下直接调用函数,this 指向 window
function fun() {
console.log(this);
}
fun(); // fun() 实际上是window.fun(), 所以this -> window2)对象函数调用,哪个对象调用就指向哪个对象 箭头函数没有 this 关键词,this 指向父作用域
var obj1 = {
a: 1,
fun1: function () {
console.log(this);
},
obj2: {
fun2: function () {
console.log(this);
},
},
};
obj1.fun1(); // fun1由obj调用,所以this -> obj1
obj1.obj2.fun2(); // fun2由obj2调用,所以this -> obj23)new 实例化对象,构造函数中的 this 指向实例对象
var Person = function () {
this.name = '小刘'; // 这里的this -> obj对象
};
var obj = new Person();4)事件中的 this 在 HTML 事件句柄中,this 指向了接收事件的 HTML 元素 <button onclick="this.style.display='none'">点我我就消失</button> 5)改变 this 的指向
4. Primitives vs. Reference Values (Objects)
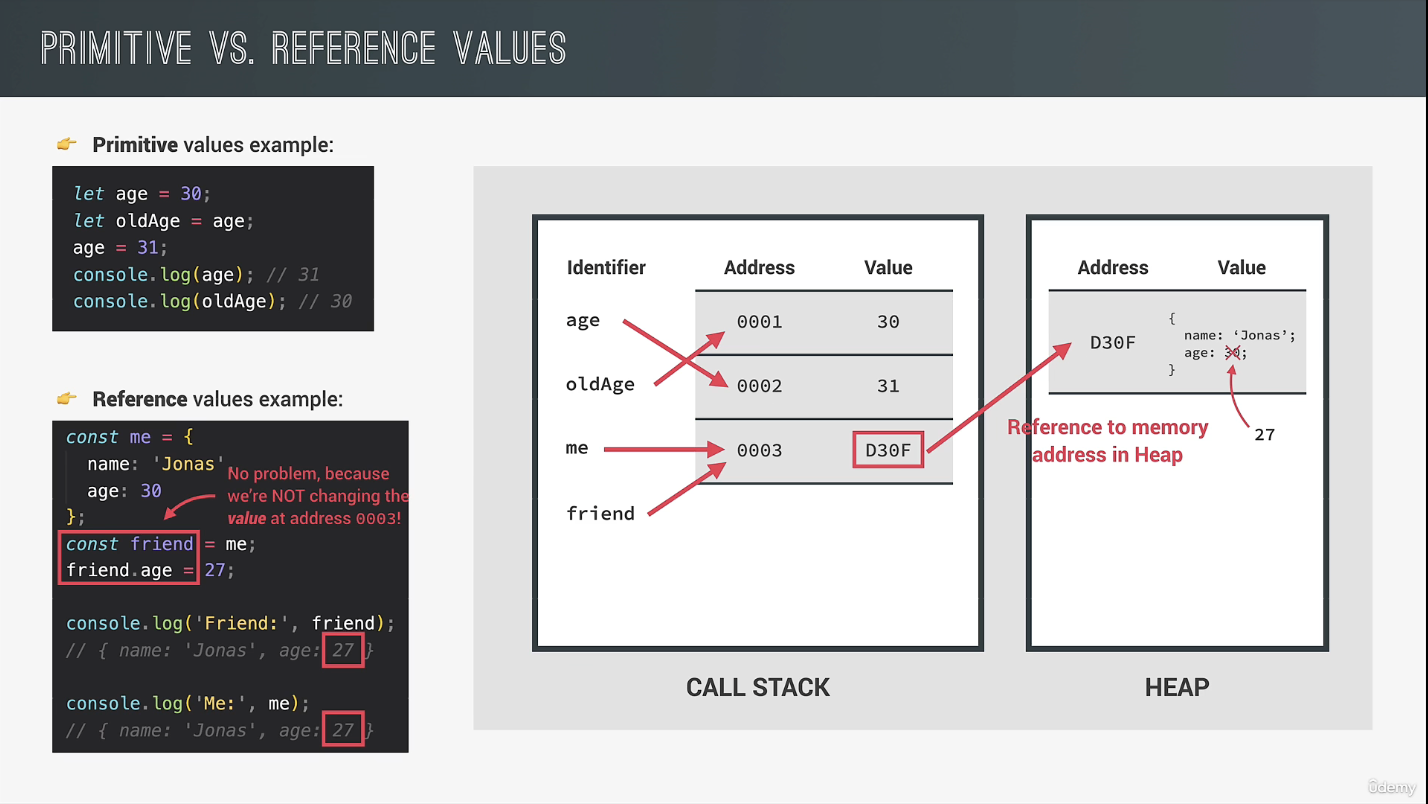 对象中的变量(属性)储存方式与其他的不同 浅拷贝
对象中的变量(属性)储存方式与其他的不同 浅拷贝 const wjCopy = Object.assign({}, wj2); 深克隆 Lo-Dash 库
Chapter 5
1. Destructuring Arrays 解构数组
const arr = [2, 3, 4];
const [x, y, z] = arr;// 2 3 4
const [a, , b] = arr;// 2 4
[a, b] = [b, a];// 不使用临时变量来交换变量值
const [i, , [j, k]] = [2, 3 , [5,6]]; // 2 5 6 解构
const [p=1, q=1, r=1] = [2, 3]; // 2 3 1 数组未知长度解构
///使用初始值来防止有undefined产生
orderDelivery({ starterIndex = 1, mainIndex = 0, time = '20:00', address }) {
console.log(
`Order received! ${this.starterMenu[starterIndex]} and ${this.mainMenu[mainIndex]} will be delivered to ${address} at ${time}`
);
}2. Spread Operators 扩展运算符
扩展运算符可以将数组中的每个元素或对象中的每个键值对取出,并且不能在模板字符串中使用。 只能用于 Iterables: arrays, strings, maps, sets. NOT objects
const arr = [7, 8, 9];
const badNewArr = [1, 2, arr[0], arr[1], arr[2]];
console.log(badNewArr); //1 2 7 8 9
const newArr = [1, 2, ...arr];
console.log(newArr); //1 2 7 8 93. Rest Pattern and Parameters
//
const [a, b, ...other] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(other); // [3, 4 , 5]// 传入多个参数
const add = function (...numbers) {
console.log(numbers);
let sum = 0;
for (let index = 0; index < numbers.length; index++) {
sum += numbers[index];
}
console.log(sum);
};
add(2, 3); // 5
add(5, 3, 7, 2); // 174. Short Circuiting 短路
console.log('' || 'shit'); // ''是falsy value 输出为shit
console.log(0 || undefined || 1 || 24 || 'shit'); // 输出第一个真值Truthy Value,为1,剩下的短路
console.log(7 && 0); // 输出为0
console.log(1 || 24 || 0 || 'shit' || 24); // 输出第一个假值Falsy Value,为0,剩下的短路
console.log(null ?? 2); // null 或 undefined 不会被0 和 ' ' 影响。 输出第一不为null 或undefined的 falsy数5. Logical Assignment Operators 逻辑分配运算符
Introduced in ES2021
const rest1 = {
name: 'capri',
numGeust: 20,
};
const rest2 = {
name: 'La',
owner: 'wjh',
};
// rest1.numGeust = rest1.numGeust || 10;
rest1.numGeust ||= 10;
// rest2.numGeust = rest2.numGeust || 10;
rest2.numGeust ||= 10;
console.log(rest1); //
console.log(rest2);??= &&= 可以用&&代替 if else
a > b && console.log('a>b');6. forof loop
for (const iterator of object) {
console.log(iterator);
}7. Enhanced Object Literals (ES6)
// 1. 定义对象时,属性可以单独定义然后直接放进去
const property1 = {
dd: 23
};
const mainObj = {
property2: 'ddd',
property1
// 2. 函数简写
order: function (index){
return index;
},
// 等于 下面的即去掉function关键词和冒号
// order (index){
// return index;
// }
// 3. 计算属性名
[array[2]] : {
fds: 2,
}
}8. Optional Chaining (可选链)
?. 链接运算符,如果前面的都不存在 直接返回 undefined
console.log(restaurant.openingHours.mon?.open);
console.log(restaurant.openingHours?.mon?.open);
console.log(restaurant.openingHours?.thu?.open);
const user = ['wj', 'xik'];
console.log(user?.[0] ?? 'no'); // wj
const user1 = [];
console.log(user?.[0] ?? 'no'); // no9. Looping objects 关于对象的循环
Object.keys(objName) 键 Object.values(objName) 值 Object.entries(objName) 键值对 obj.property.entries()
10. Sets 集
没有重复的值,需要传入可迭代(string,array),没有键值对,没有 index(不能写set1[0])。 主要作用: const setExample = new Set(iterable)
const ordersSet = new Set([
'Pasta',
'Pizza',
'Pizza',
'Risotto',
'Pasta',
'Pizza',
]);
console.log(ordersSet); //{'Pasta', 'Pizza', 'Risotto'}
console.log(new Set('Jonas')); //{'J', 'o', 'n', 'a', 's'}
console.log(ordersSet.size); // 3
console.log(ordersSet.has('Pizza')); // true
console.log(ordersSet.has('Bread')); // false
ordersSet.add('Garlic Bread');
ordersSet.add('Garlic Bread');
ordersSet.delete('Risotto');
// ordersSet.clear(); // {}
console.log(ordersSet); // {'Pasta', 'Pizza', 'Garlic Bread'}
// for (const order of ordersSet) console.log(order);
const staff = ['Waiter', 'Chef', 'Waiter', 'Manager', 'Chef', 'Waiter'];
const staffUnique = [...new Set(staff)];
console.log(staffUnique); // ['Waiter', 'Chef', 'Manager']
console.log(
new Set(['Waiter', 'Chef', 'Waiter', 'Manager', 'Chef', 'Waiter']).size
); // 3
console.log(new Set('jonasschmedtmann').size); // 11,一种计算string的长度的方法11. Maps 字典
objects 中的 key 基本上都是 string,但 maps 中的 key 可以为各种类型(objects arrays maps)
const rest = new Map();
rest.set('name', 'Classico Italiano');
rest.set(1, 'Firenze, Italy');
console.log(rest.set(2, 'Lisbon, Portugal'));
rest
.set('categories', ['Italian', 'Pizzeria', 'Vegetarian', 'Organic'])
.set('open', 11)
.set('close', 23)
.set(true, 'We are open :D')
.set(false, 'We are closed :(');
console.log(rest.get('name')); // Classico Italiano
console.log(rest.get(true)); // We are open :D
console.log(rest.get(1)); // We are closed :(
const time = 8;
console.log(rest.get(time > rest.get('open') && time < rest.get('close'))); // time > rest.get('open') && time < rest.get('close') 如果为真 打印 We are open :D
console.log(rest.has('categories')); // true
rest.delete(2);
// rest.clear();
const arr = [1, 2];
rest.set(arr, 'Test');
// rest.get([1,2]) 会返回undefined因为在堆中,这两个数组不是同一个地址
rest.set(document.querySelector('h1'), 'Heading');
console.log(rest.get(arr)); // Test// Maps: Iteration
const question = new Map([
['question', 'What is the best programming language in the world?'],
[1, 'C'],
[2, 'Java'],
[3, 'JavaScript'],
['correct', 3],
[true, 'Correct 🎉'],
[false, 'Try again!'],
]);
console.log(question);
// Convert object to map
console.log(Object.entries(openingHours));
const hoursMap = new Map(Object.entries(openingHours));
console.log(hoursMap);
// Quiz app
console.log(question.get('question'));
for (const [key, value] of question) {
if (typeof key === 'number') console.log(`Answer ${key}: ${value}`);
}
// const answer = Number(prompt('Your answer'));
const answer = 3;
console.log(answer);
console.log(question.get(question.get('correct') === answer));
// Convert map to array
console.log([...question]);
// console.log(question.entries());
console.log([...question.keys()]);
console.log([...question.values()]);12. Which data structure?
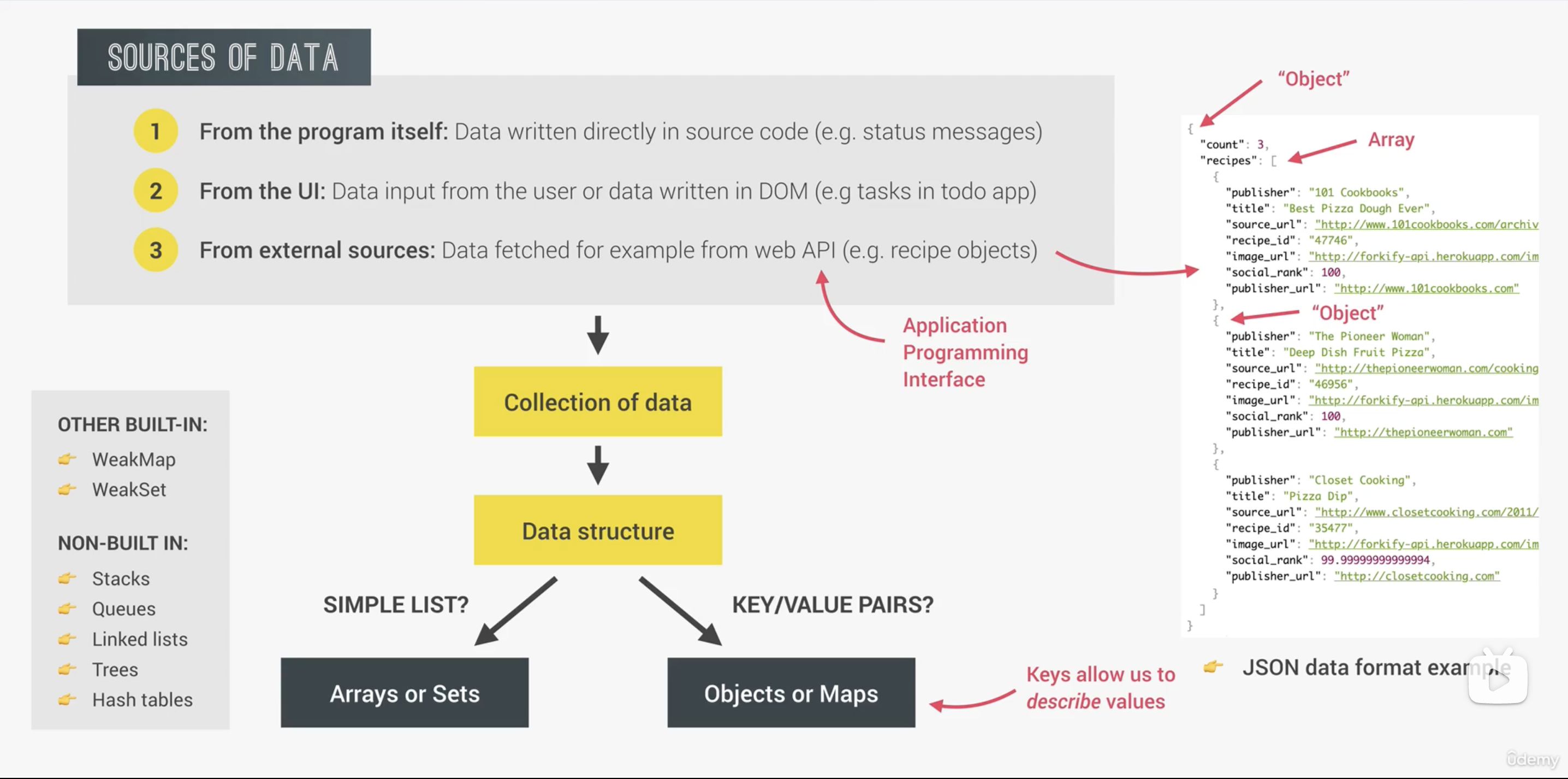

13. Working with Strings
const airline = 'TAP Air Portugal';
const plane = 'A320';
// position
console.log(airline[2]); // P
console.log('wjsb'[1]); // j
// length method
console.log(airline.length); //16
console.log('wjsb'.length); // 4
// indexOf method
console.log(airline.indexOf('r')); // 6
console.log(airline.lastIndexOf('r')); // 10
console.log(airline.indexOf('Portugal')); // 8
// slice 切片 获得substring [start,end) 结尾不算进去 substring长度 = end - start
console.log(airline.slice(4)); // Air Portugal
console.log(airline.slice(4, 7)); // Air
// 提取第一个单词,以空格的index为end参数
console.log(airline.slice(0, airline.indexOf(' ')));
// 提取最后一个单词,以空格的lastindex + 1为start参数
console.log(airline.slice(airline.lastIndexOf(' ') + 1));
// 是否选到中间座位
const checkMiddleSeat = function (seat) {
// B and E are middle seats
const s = seat.slice(-1);
if (s === 'B' || s === 'E') console.log('You got the middle seat 😬');
else console.log('You got lucky 😎');
};
checkMiddleSeat('11B');
checkMiddleSeat('23C');
checkMiddleSeat('3E');
const airline = 'TAP Air Portugal';
console.log(airline.toLowerCase()); // tap air portugal
console.log(airline.toUpperCase()); // TAP AIR PORTUGAL
// Fix capitalization in name
const passenger = 'jOnAS';
const passengerLower = passenger.toLowerCase(); // jonas
const passengerCorrect =
passengerLower[0].toUpperCase() + passengerLower.slice(1);
console.log(passengerCorrect); // Jonas
// tirm method 修剪字符串 去掉空格以及换行符
const email = 'hello@jonas.io';
const loginEmail = ' Hello@Jonas.Io \n';
// const lowerEmail = loginEmail.toLowerCase();
// const trimmedEmail = lowerEmail.trim();
const normalizedEmail = loginEmail.toLowerCase().trim();
console.log(normalizedEmail);
console.log(email === normalizedEmail);
// replace method
const priceGB = '288,97£';
const priceUS = priceGB.replace('£', '$').replace(',', '.');
console.log(priceUS);
const announcement =
'All passengers come to boarding door 23. Boarding door 23!';
console.log(announcement.replace('door', 'gate'));
console.log(announcement.replaceAll('door', 'gate'));
console.log(announcement.replace(/door/g, 'gate'));
// Booleans
const plane = 'Airbus A320neo';
console.log(plane.includes('A320'));
console.log(plane.includes('Boeing'));
console.log(plane.startsWith('Airb'));
if (plane.startsWith('Airbus') && plane.endsWith('neo')) {
console.log('Part of the NEW Airbus family');
}
// Practice exercise
const checkBaggage = function (items) {
const baggage = items.toLowerCase();
if (baggage.includes('knife') || baggage.includes('gun')) {
console.log('You are NOT allowed on board');
} else {
console.log('Welcome aboard!');
}
};
checkBaggage('I have a laptop, some Food and a pocket Knife');
checkBaggage('Socks and camera');
checkBaggage('Got some snacks and a gun for protection');
// Split and join
console.log('a+very+nice+string'.split('+'));
console.log('Jonas Schmedtmann'.split(' '));
const [firstName, lastName] = 'Jonas Schmedtmann'.split(' ');
// join method
const newName = ['Mr.', firstName, lastName.toUpperCase()].join(' ');
console.log(newName);
const capitalizeName = function (name) {
const names = name.split(' ');
const namesUpper = [];
for (const n of names) {
// namesUpper.push(n[0].toUpperCase() + n.slice(1));
namesUpper.push(n.replace(n[0], n[0].toUpperCase()));
}
console.log(namesUpper.join(' '));
};
capitalizeName('wang xiangkun');
capitalizeName('jonas schmedtmann');
// Padding 填充 padStart(整个字符串的长度,要添加的字符)
const message = 'Go to gate 23!';
console.log(message.padStart(20, '+').padEnd(30, '+'));
console.log('Jonas'.padStart(20, '+').padEnd(30, '+'));
const maskCreditCard = function (number) {
const str = number + '';
const last = str.slice(-4);
return last.padStart(str.length, '*');
};
console.log(maskCreditCard(64637836));
console.log(maskCreditCard(43378463864647384));
console.log(maskCreditCard('334859493847755774747'));
// repeat method
const message2 = 'Bad waether... All Departues Delayed... ';
console.log(message2.repeat(5));
const planesInLine = function (n) {
console.log(`There are ${n} planes in line ${'🛩'.repeat(n)}`);
};
planesInLine(5);
planesInLine(3);
planesInLine(12);装箱
Strings are primitives, why do they have methods? Shouldn't methods only be available on objects such as a race? JavaScript will automatically behind the scenes convert that string primitive to a string object with the same content. -- boxing
// Boxing 装箱
console.log(new String('jonas'));
console.log(typeof new String('jonas')); // object
console.log(typeof new String('jonas').slice(1)); // stringChapter 6 Functions
1. How Passing Arguments Works: Values vs. Reference 值传递
js 中只有按值传递(passing by value),没有按参考传递(passing by reference)。对传入函数的对象来说,传入的内存地址,也只是一个包含内存地址的值。具体参考内存章节。
const flight = 'LH234';
const jonas = {
name: 'Jonas Schmedtmann',
passport: 24739479284,
};
const checkIn = function (flightNum, passenger) {
flightNum = 'LH999'; //无效 跟形参不是一个地址,只是单纯的复制了值
passenger.name = 'Mr. ' + passenger.name; // 有效 复制了值,但这个值的内容是地址,因此改变的还是原来heap里的那个jonas对象
};2. First-Class functions 函数一等优先 vs Higer-order functions 高阶函数
First-class Function(头等函数) 当一门编程语言的函数可以被当作变量一样用时,则称这门语言拥有头等函数。 js 里的函数就是值,可以被当作参数传递给其他函数,可以作为另一个函数的返回值,还可以被赋值给一个变量。函数是 js 对象中的一种,对象大多数都有方法,例如 function.name()。 高阶函数是至少具有下列功能之一的函数: 1. 将一个或多个函数作为参数(即过程参数)。 2. 返回一个函数作为结果。 所有其他函数都是一阶函数。

3. 高阶函数 回调函数
const oneWord = function (str) {
return str.replace(/ /g, '').toLowerCase();
};
const upperFirstWord = function (str) {
const [first, ...others] = str.split(' ');
return [first.toUpperCase(), ...others].join(' ');
};
// Higher-order function
const transformer = function (str, fn) {
// transformer 调用其他函数,为高阶函数,面对对象编程中重要的一环;调用的function被称为回调函数 callback functions
console.log(`Original string: ${str}`);
console.log(`Transformed string: ${fn(str)}`);
console.log(`Transformed by: ${fn.name}`);
};
transformer('JavaScript is the best!', upperFirstWord); // 回调函数
transformer('JavaScript is the best!', oneWord); // 回调函数4. 函数返回函数
const greeterHey = greet('Hey'); // greet()的结果是返回一个函数,所以现在greeterHey也是一个函数,就是greet()返回的那个函数,参数是name。因此greeterHey = function (name) {console.log(`${greeting} ${name}`);};
greeterHey('Jonas'); // Hey Jonas
greeterHey('Steven'); // Hey Steven
greet('Hello')('Jonas'); // Hello Jonas
const greet1 = greeting => name => console.log(`${greeting} ${name}`);
greet1('hello')('shit'); // hello shit5. Call and apply method
const lufthansa = {
airline: 'Lufthansa',
iataCode: 'LH',
bookings: [],
// book: function () {}
book(flightNum, name) {
console.log(
`${name} booked a seat on ${this.airline} flight ${this.iataCode}${flightNum}`
);
this.bookings.push({
flight: `${this.iataCode}${flightNum}`,
name,
});
},
};
lufthansa.book(239, 'Jonas Schmedtmann');
lufthansa.book(635, 'John Smith');
const eurowings = {
airline: 'Eurowings',
iataCode: 'EW',
bookings: [],
};
const book = lufthansa.book;
// Does NOT work
// book('123', 'shit');
//this keyword depends on how the function is called.
//所以在这里调用book(),this指向的是window,因此this.airline是undefined,this.iataCode是undefined,this.bookings是undefined
// Call method
book.call(eurowings, 23, 'Sarah Williams'); // 手动设置this指向eurowings,因此this.airline是eurowings,this.iataCode是EW,this.bookings是eurowings.bookings
book.call(lufthansa, 239, 'Mary Cooper');
// lufthansa.book.call(lufthansa, 239, 'Mary Cooper'); 结果与上面一样
// Apply method
const flightData = [583, 'George Cooper'];
book.apply(eurowings, flightData); // apply()的第二个参数是一个数组,其余与call()一样,但由于es6加入了扩展运算符,所以一般不用apply()了,而是用:
book.call(eurowings, ...flightData);6. bind method
// Bind method
book.call(eurowings, 23, 'Sarah Williams');
const bookEW = book.bind(eurowings); // bind()返回一个新的函数,这个函数的this指向bind()的第一个参数.
const bookLH = book.bind(lufthansa);
const bookLH23 = book.bind(lufthansa, 23); // bind()的第二个参数是23,因此调用bookLH23时只需要传入一个参数,即name. 固定函数的第一个传入参数为23
bookLH(23, 'Steven Williams');
bookLH23('Steven Williams');
// With event listeners
lufthansa.planes = 300;
lufthansa.buyPlane = function () {
console.log(this);
this.planes++;
console.log(this.planes);
};
document
.querySelector('.buy')
.addEventListener('click', lufthansa.buyPlane.bind(lufthansa));
// .addEventListener('click', lufthansa.buyPlane());? why
// Partial application
const addTax = (rate, value) => value + value * rate;
console.log(addTax(0.1, 200)); // 220
const addVAT = addTax.bind(null, 0.23); // bind()的第一个参数是null,因为addTax()的this没有用到,所以可以传入null,第二个参数是0.23,即rate
// 用函数return函数写一遍
const addVATrate = function (rate) {
return function (value) {
return value + value * rate;
};
};
const addVAT1 = addVATrate(0.23); //类似解构 固定住rate的值
console.log(addVAT1(100)); //1237. Immediately Invoked Function Expressions(IIFE) 立即调用函数表达式
// IIFE 立即执行函数
(function () {
console.log('This will never run again');
const isPrivate = 23; //私有变量
})();
// console.log(isPrivate); //报错
(() => console.log('This will ALSO never run again'))(); //立即执行函数 箭头
{
const isPrivate = 23;
var notPrivate = 46;
}
// console.log(isPrivate); //报错
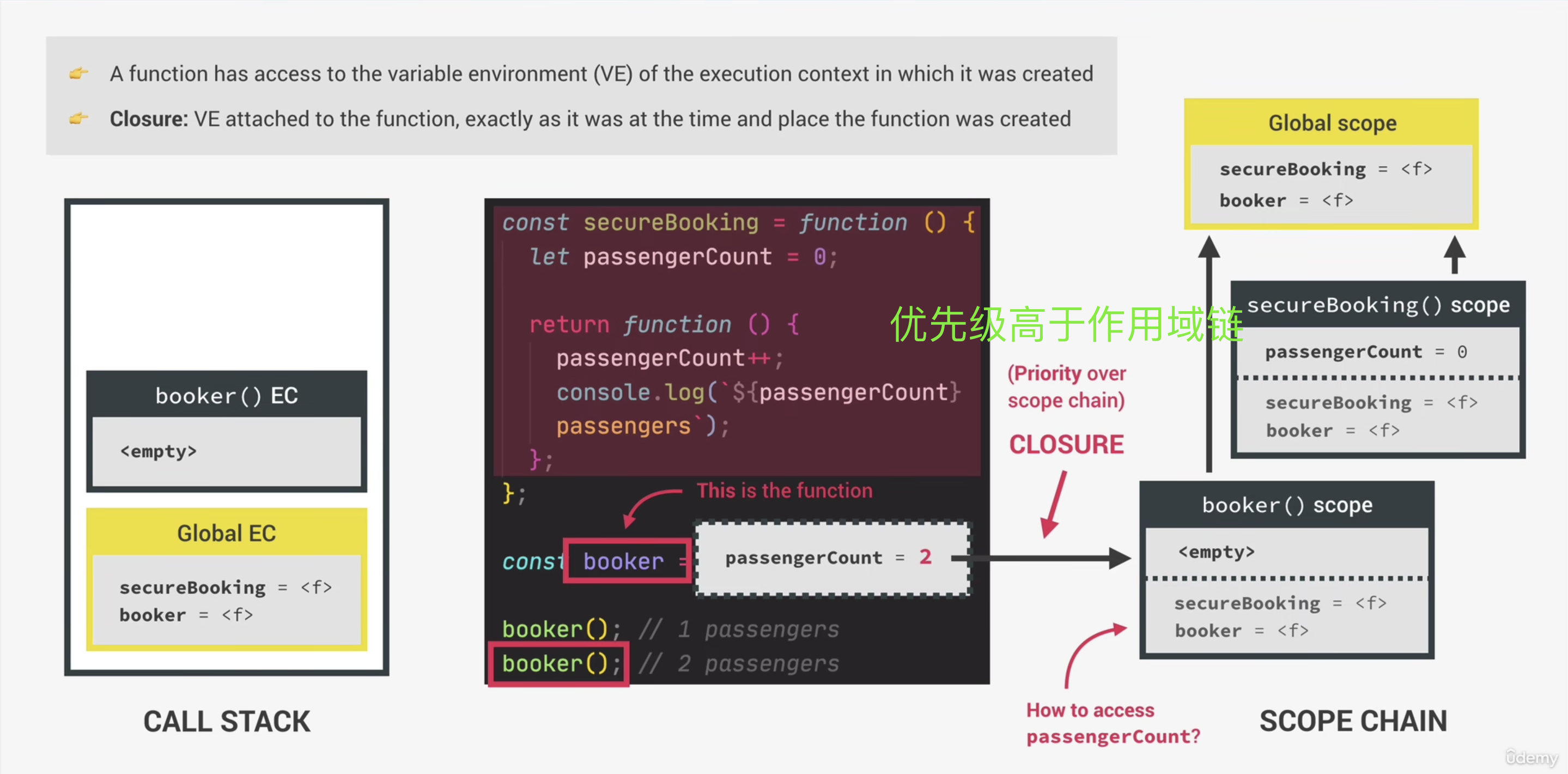
console.log(notPrivate); //468. Closures 闭包
// Closures
const secureBooking = function () {
let passengerCount = 0;
return function () {
passengerCount++;
console.log(`${passengerCount} passengers`);
};
};
const booker = secureBooking();
booker();
booker();
booker(); secureBooking() return function 后,它的执行上下文出栈,但 secureBooking()出栈后,为什么 booker()还能继续访问 passengerCount,使它累加? We can say a closure makes a function remember all the variable that existed at the function's birthplace essentially.
secureBooking() return function 后,它的执行上下文出栈,但 secureBooking()出栈后,为什么 booker()还能继续访问 passengerCount,使它累加? We can say a closure makes a function remember all the variable that existed at the function's birthplace essentially.
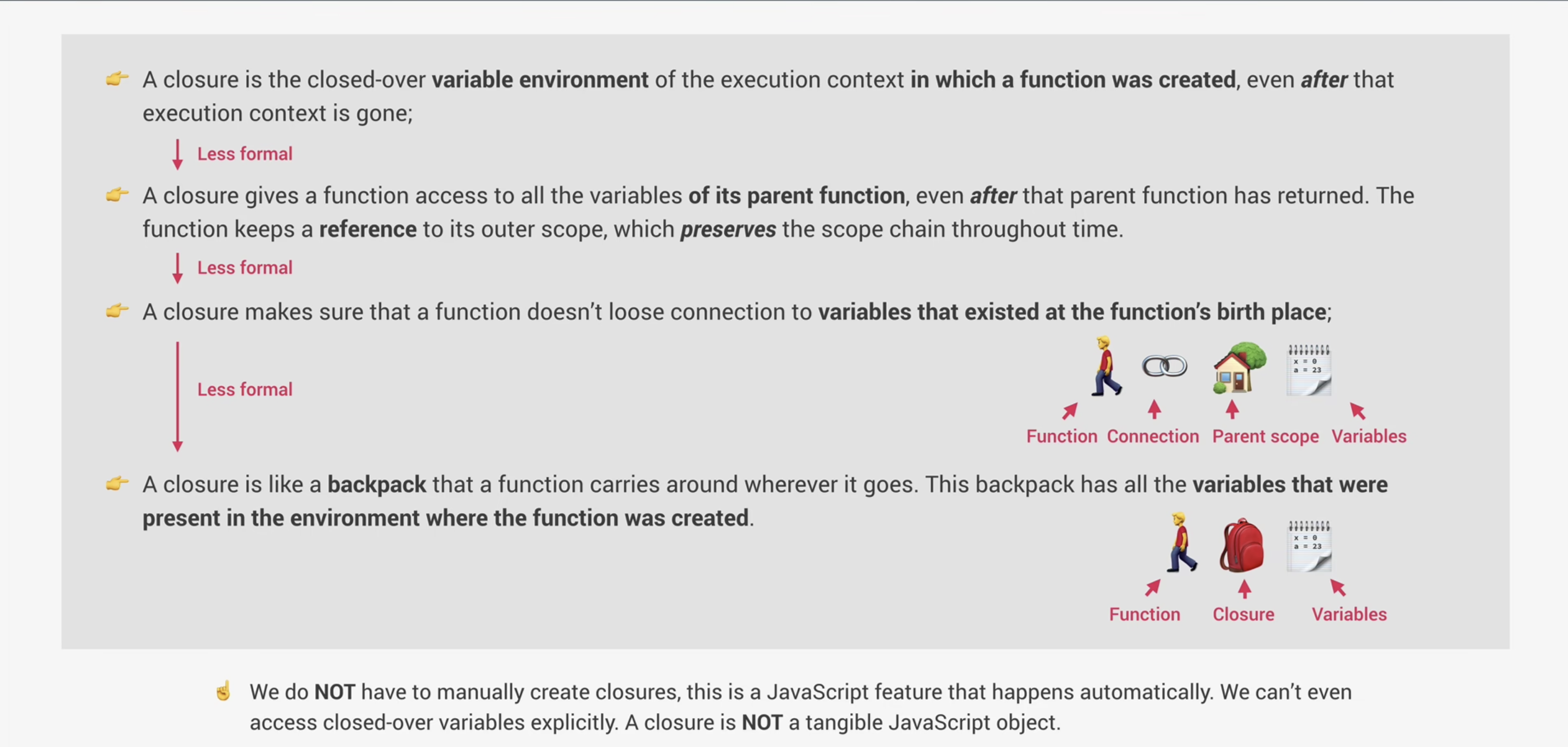 闭包就像函数的一个背包,里面包含了函数被创建时的环境里的所有的变量。但闭包不能从代码访问,可以用 console.dir()看。
闭包就像函数的一个背包,里面包含了函数被创建时的环境里的所有的变量。但闭包不能从代码访问,可以用 console.dir()看。
Chapter 7 Arrays
1. Simply Array methods
let arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'];
// SLICE 切片
console.log(arr.slice(2)); // c d e
console.log(arr.slice(2, 4)); // c d
console.log(arr.slice(-2)); // d e
console.log(arr.slice(-1)); // e
console.log(arr.slice(1, -2)); // b c
console.log(arr.slice()); // a b c d e
console.log([...arr]); // a b c d e
// slice() 和 ...arr 都是浅拷贝 都不会修改原数组
// SPLICE 拼接
// 会修改原数组 而且第二个参数为长度,不是endIndex
// 主要用来删除数组元素
arr.splice(-1); // e
console.log(arr); // a b c d
// arr.splice(, ); // b c
console.log(arr); // a b c
let arr1 = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j'];
arr1.splice(5, 2); // f g
console.log(arr1); // a b c d e h i j
arr1.splice(5, 2, 'f', 'g'); // 如果第二个参数为0,即可实现插入元素
console.log(arr1); // a b c d e f g j
// REVERSE
// 会修改原数组
arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'];
const arr2 = ['j', 'i', 'h', 'g', 'f'];
console.log(arr2.reverse());
console.log(arr2);
// CONCAT concatenate 连接 串联
// 不会修改原数组
const letters = arr.concat(arr2);
console.log(letters);
console.log([...arr, ...arr2]);
// JOIN
console.log(letters.join(' - '));2. at() method
// The new at Method
const arr = [23, 11, 64];
console.log(arr[0]);
console.log(arr.at(0));
// getting last array element
console.log(arr[arr.length - 1]);
console.log(arr.slice(-1)[0]);
console.log(arr.at(-1)); // 最简洁
console.log('jonas'.at(0));
console.log('jonas'.at(-1));3. forEach()
const movements = [200, 450, -400, 3000, -650, -130, 70, 1300];
for (const [i, movement] of movements.entries()) {
if (movement > 0) {
console.log(`Movement ${i + 1}: You deposited ${movement}`);
} else {
console.log(`Movement ${i + 1}: You withdrew ${Math.abs(movement)}`);
}
}
// forEach是高阶函数,需要一个回调函数,函数参数是forEach传入的每一个element, index, array. 顺序固定。forEach不会返回任何值,无法break,continue,return
movements.forEach(function (movement, i, arry) {
if (movement > 0) {
console.log(`Movement ${i + 1}: You deposited ${movement}`);
} else {
console.log(`Movement ${i + 1}: You withdrew ${Math.abs(movement)}`);
}
});
// 0: function(200)
// 1: function(450)
// 2: function(400)
// ...
// Map
const currencies = new Map([
['USD', 'United States dollar'],
['EUR', 'Euro'],
['GBP', 'Pound sterling'],
]);
// array都是本身,不是每次循环的一列!
currencies.forEach(function (el, i, array) {
console.log(`${i}: ${el}`);
console.log(array);
});
// Set
const currenciesUnique = new Set(['USD', 'GBP', 'USD', 'EUR', 'EUR']);
console.log(currenciesUnique);
// 由于Set没有index,为了保持参数的一致性,这里index=value
currenciesUnique.forEach(function (el, i, array) {
console.log(`${i}: ${el}`);
console.log(array);
});4. Data Transformation map()映射, filter, reduce
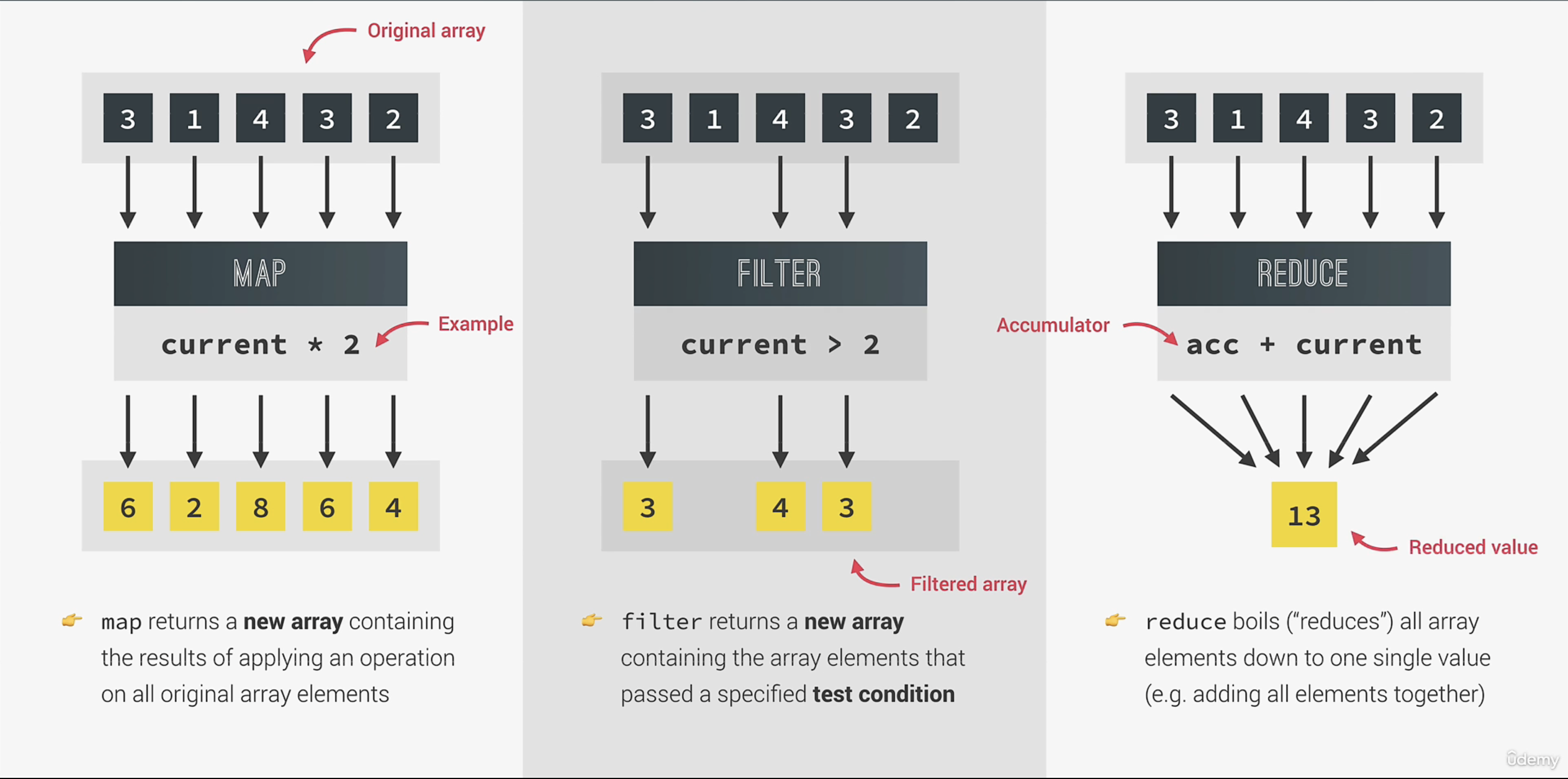
// filter
// const deposit = movements.filter(mov => mov > 0);
const deposit = movements.filter(function (mov) {
return mov > 0;
});
console.log(movements);
console.log(deposit);
const withdrawals = movements.filter(mov => mov < 0);
console.log(withdrawals);
// reduce
//accumulator -> snowball 累加
const balance = movements.reduce(function (accumulator, current, index, arr) {
console.log(index, accumulator);
return accumulator + current;
}, 0);
// maximum value using reduce
const max = movements.reduce((acc, cur) => {
if (acc > cur) return acc;
else return cur;
}, movements[0]); // 使用reduce来求最大值时,第一个返回值要注意不要设成0
console.log(max);5. find() method
// find 返回找到的第一个
const firstWithdrawl = movements.find(el => el < 0);
console.log(firstWithdrawl);6. some() method and every() method
// some() method
// 与includes()不同,some()可以判断条件,比等式范围更大
console.log(movements);
console.log(movements.some(el => el > 0)); // true
// every
console.log(movements.every(el => el > 0)); // false
console.log(movements.every(el => typeof el === 'number')); // true7. flat() and flatMap()
const arr = [1, [2, 3], 4];
const arr1 = [1, [2, 3, [4, 5], 6], 7];
console.log(arr.flat()); //1234
console.log(arr1.flat()); //123[4,5]67
console.log(arr1.flat(2)); //1234567 Depth 参数
// const accountsMovenment = accounts.map(el => el.movements);
// console.log(accountsMovenment);
// const allMovement = accountsMovenment.flat();
// console.log(allMovement);
// const overalBalance = allMovement.reduce((acc, el) => acc + el);
// console.log(overalBalance);
// const overalBalance2 = accounts
// .map(el => el.movements)
// .flat()
// .reduce((acc, el) => acc + el);
// console.log(overalBalance2);
const overalBalance2 = accounts
.flatMap(el => el.movements) // flatMap 只能一层深度, = .map().flat()
.reduce((acc, el) => acc + el);
console.log(overalBalance2);8. Sorting array
其他
带 sourcemap 打包,然后将 sourcemap 删除掉再上线 跨域问题来自于浏览器的同源策略,即当协议、域名、端口号任意一个不同时,都会引发跨域问题。
算法
node: 输入: let str = readline();
字符串
字符串切片
slice(start, end)只能传入切片开头和结尾的 index,不能固定切片长度,index 可以为负数,但 start 不可以大于 end; 第一个参数比第二个参数大,结果返回空字符串; 传入参数是负数,slice()会先做运算 test.length + 负数参数。substr(start, length)从 start 开始,返回 length 长度字符,支持负数,不支持数组。传入参数超过 length 返回空字符 串; 传入负数,则从字符串的尾部开始算起始位置,-1 指最后一个字符,-2 指倒数第二个字符; 当传入的第一个参数是负数且它的绝对值超过 length,这个负数转化为 0,当传入的第二个参数是负数,等价于 0,截取 0 个字符,返回空字符串。substring(start, stop)第二个参数==第一个参数,返回空字符串; 传入两个参数,不管在第一还是第二位置,都会将小的参数作为第一个参数,较大的作为第二个参数; 任何一个参数为负数或者 NaN 的时候,自动将其转换为 0; 任何一个参数大于 length,按照 length 处理; 只传入一个参数时,为 start。split(separator, length)join(separator)splice(start, length, …args)
字符串填充
string.padEnd(targetLength, padString)
进制转换
parseInt(num, 16) 转换 16 进制 Number(string)
-parseInt(num, 8); //八进制转十进制
-parseInt(num, 16); //十六进制转十进制
-parseInt(num).toString(8) - //十进制转八进制
parseInt(num).toString(16) - //十进制转十六进制
parseInt(num, 2).toString(8) - //二进制转八进制
parseInt(num, 2).toString(16) - //二进制转十六进制
parseInt(num, 8).toString(2); //八进制转二质数因子
取余,% 1.判断终止条件: sqrt(num) 2.本身就是质数的情况 从 2 开始, 如果余数为 0, 继续除当前(包括重复的质因子)就行
数组去重
重复元素在 Set 中自动被过滤
var s = new Set([1, 2, 3, 3, '3']);
s; // Set {1, 2, 3, "3"}排序
sort() 方法中有一个参数,非必填,但是在忽略此参数的情况下,使用 sort()排序会默认先调用数组中每一项元素的 toString()方法,然后根据首字母的 ASCLL 码值的大小进行排序。
//升序 // sort((a,b)=>{return a-b;})
arr.sort(function(x,y){
retun x-y;
});
//降序
arr.sort(function(x,y){
retun y-x;
});字符串替换
str.replace(/[(a-z)]/g, a =>{...}
let text = readline();
const arr = [
'abc',
2,
'def',
3,
'ghi',
4,
'jkl',
5,
'mno',
6,
'pqrs',
7,
'tuv',
8,
'wxyz',
9,
];
text = text.replace(/[(a-z)]/g, a => {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (typeof arr[i] == 'string' && arr[i].indexOf(a) != -1) {
return arr[i + 1];
}
}
});
text = text.replace(/([A-Z])/g, a => {
if (a == 'Z') {
return 'a';
} else {
return String.fromCharCode(a.toLowerCase().charCodeAt(0) + 1);
}
});
console.log(text);统计字符串出现次数
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
if (obj[str[i]]) obj[str[i]]++;
else obj[str[i]] = 1;
} // 输入aabcddd {a:2 b: 1 c:1 d:3}
// 找到出现次数最少的字符串,不拼接它们(删除)
let min = Math.min(...Object.values(obj));
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
if (obj[str[i]] !== min) res += str[i];
}素数
function isPrime(num) {
for (let i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i++) {
if (num % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}生成 [x, y]之间的随机整数
function getRandom(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
}
console.log(getRandom(1, 10));
//生成 [0, x) 之间的随机数
Math.round(Math.random() * x);
//生成 [x, y) 之间的随机数
Math.round(Math.random() * (y - x) + x);