Node.js
Nodejs
Section 1
Nodejs 为什么适合后端

Beginning Code
const fs = require('fs'); // fileSystem
const hello = 'hello world!';
console.log(hello);
const textIn = fs.readFileSync('1-node-farm/starter/txt/input.txt', 'utf-8');
console.log(textIn);
const textOut = `This is what we know about the avocado ${textIn}`;
fs.writeFileSync('1-node-farm/starter/txt/output.txt', textOut);
console.log('file ok');相对地址不能用./写法,不知道为什么,但 nodejs 推荐绝对路径写法。
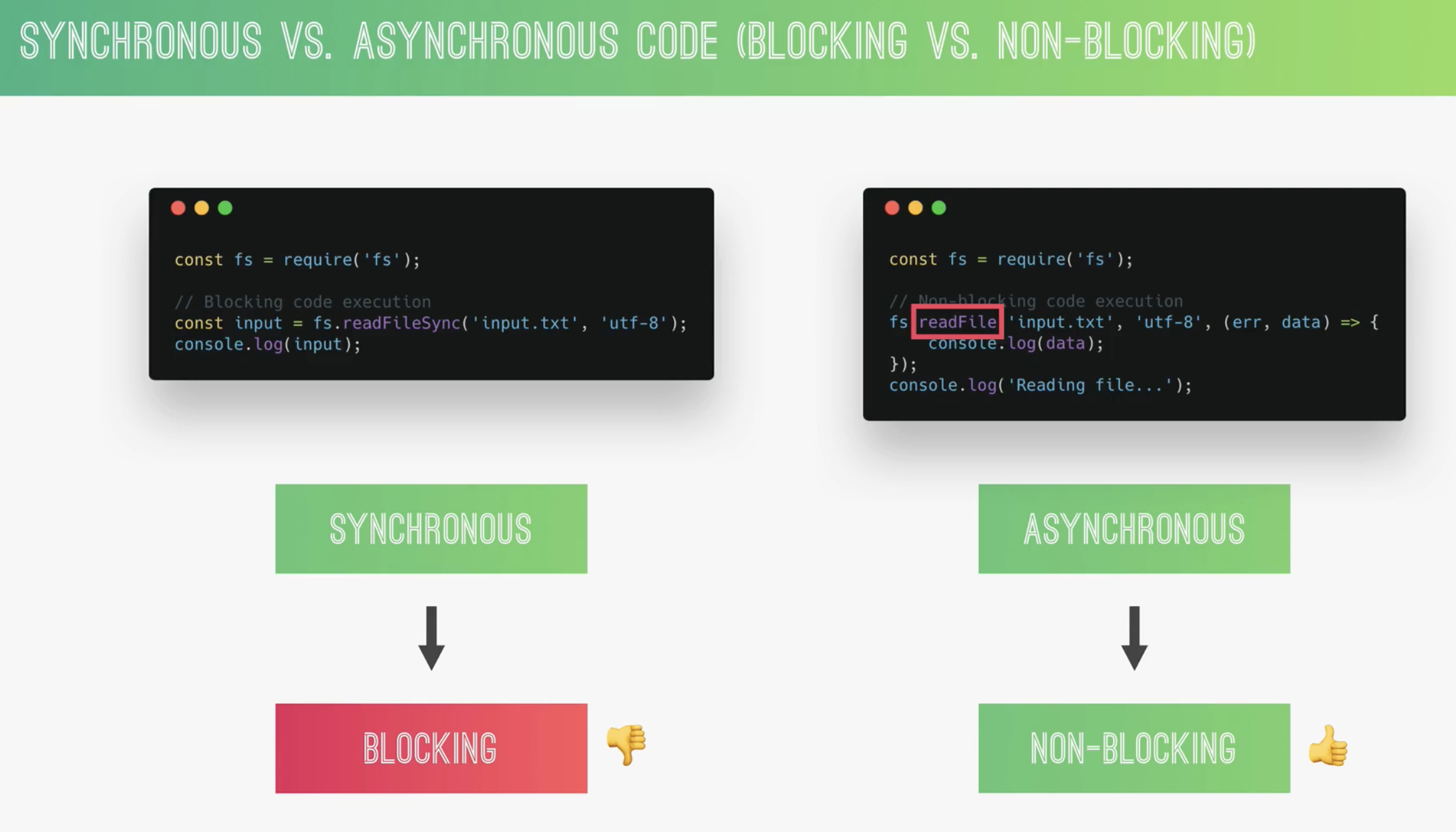
synchronous 和 asynchronous
nodejs 是单线程的,同步代码也叫阻塞代码。
Nodejs 基于 callback
CommonJS
导出:module.export = ...
导入: const xx = require('包名或者目录')
如果你想在 Node.js 中使用 ES6 的 import 和 export,你需要确保你的 Node.js 版本是 13.2.0 或更高。然后,你可以在你的 package.json 文件中添加 "type": "module",或者将你的文件扩展名改为 .mjs。例如:
import replaceTemplate from './modules/replaceTemplate.js';
export default replaceTemplate;请注意,如果你选择使用 ES6 模块,你可能需要更新你的代码以适应新的语法,因为 ES6 模块和 CommonJS 模块在某些方面有所不同。
fileSystem(fs)
const fs = require('fs'); // fileSystem
const tempOverview = fs.readFileSync(
`${__dirname}/templates/template-overview.html`,
'utf-8'
);__dirname 是 Node.js 环境的全局变量,它表示当前执行脚本所在的目录。它是一个字符串,包含了完整的绝对路径。
readFileSync 同步读取文件,会阻塞代码,但一般是读取一定要发送的数据,且只读取一次。
http
http.creatServer 来创建服务器,server.listen来监听端口。
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
console.log(req.url);
// const pathname = req.url;
// 获得路由query参数和地址
const { query, pathname } = url.parse(req.url, true);
// 路由判断返回页面
// Overview
if (pathname === '/overview' || pathname === '/') {
// 返回头
res.writeHead(200, {
'content-type': 'text/html',
});
const cardsHtml = dataObj
.map(el => replaceTemplate(tempCard, el))
.join(' ');
console.log(cardsHtml);
const output = tempOverview.replace(/{%PRODUCT_CARDS%}/g, cardsHtml);
res.end(output);
}
// product
else if (pathname === '/product') {
const product = dataObj[query.id];
res.writeHead(200, {
'content-type': 'text/html',
});
const output = replaceTemplate(tempProduct, product);
res.end(output);
} else if (pathname === '/api') {
console.log(__dirname);
res.writeHead(200, {
'content-type': 'application/json',
});
res.end(data);
} else {
res.writeHead(404, {
'content-type': 'text/html',
});
res.end('<h1>Page not found</h1>');
}
});
server.listen(8000, '127.0.0.1', () => {
console.log('Server is listening on port 8000');
});npm
npm init 来初始化,生成 package.json
npm install 来安装包
npm run start或npm start 运行nodemon index.js 脚本由自己编写,nodemon 是热加载插件。
https://www.npmjs.com/ 查询 package 用法
{
"name": "node-farm-starter",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "nodemon index.js"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"nodemon": "^3.0.3"
},
"dependencies": {
"slugify": "^1.6.6"
}
}Section 2
TCP/IP
HTTP
Section 3
Node architecture
Thread Pool
nodejs 单线程,但是 libuv 提供 4 个线程(最多可以分为 128 个),来处理 EventLoop 里过于繁重的任务。
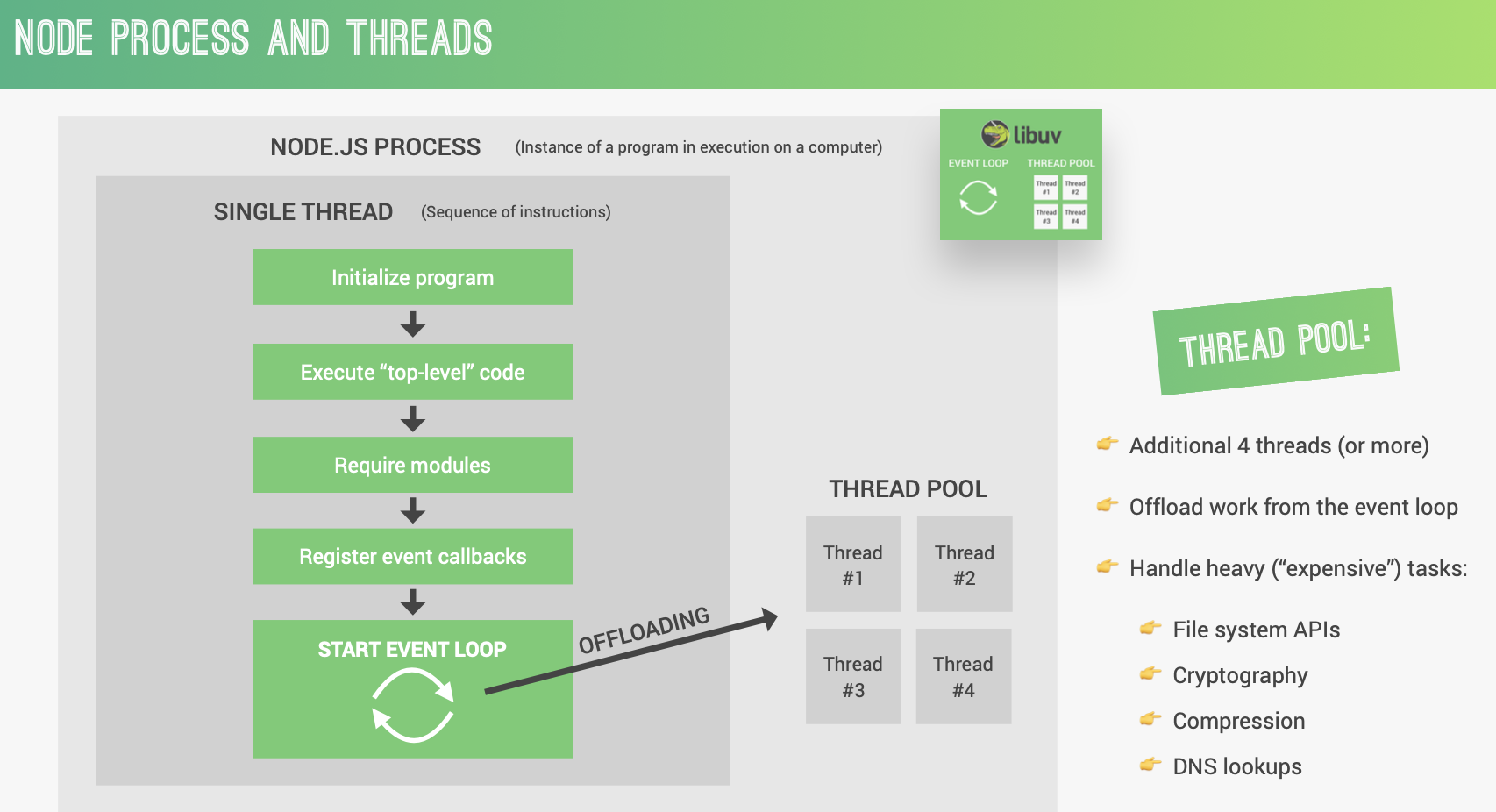
Event Loop
Section 4
Express
Middleware
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('Hello from the middleware 👋');
req.requestTime = new Date().toISOString();
next();
});Q: 一个中间件在调用下一个中间件时,req 也会继续传递下去吗?
A: 是的,当你在一个中间件中调用next()函数时,请求(req)对象会被传递到下一个中间件。
在 Express 中,中间件函数有访问请求对象(req),响应对象(res),和应用程序的请求-响应周期中的下一个中间件函数的能力,通常由名为next的变量表示。
当一个中间件函数接收到请求和响应对象时,它可以修改这些对象。修改会被保留并传递到请求-响应周期中的下一个中间件或路由处理器。
例如,在你的代码中,你在req对象上添加了一个user属性:
req.user = currentUser;
这个user属性会被添加到req对象,并在后续的中间件中可用。所以,当你在这个中间件中调用next()时,下一个中间件会接收到包含user属性的req对象
router
param middleware
MongoDB
Section 5
Connect MongoDB
Mongoose
类似 mybatis,帮助操作数据库
查询返回的是Query对象,原型上有很多方法。
Tour.find(queryObj)返回一个 Query 对象,这是一个可以被链式调用的对象,它不会立即执行数据库查询。只有当你调用一个执行方法(如.exec())或者当你使用await关键字时,查询才会被执行。
Pagination
const page = req.query.page * 1 || 1;
const limit = req.query.limit * 1 || 10;
const skip = (page - 1) * limit;
query = query.skip(skip).limit(limit);可用插件:mongoose-paginate-v2,约等于 Java 的 pageHelper,还未尝试。
Aggregation Pipline
类似聚合函数+窗口函数+子查询
MongoDB 的特性,但可以通过 Mongoose 的 Model 访问。
fat model, thin controller
Error Handling
unhandledRejections
process.on('unhandledRejection', (err) => {
console.log(err.name, err.message);
console.log('UnhandledRejection💥');
server.close(() => {
process.exit(1);
});
});uncaughtExceptions
process.on('uncaughtException', (err) => {
console.log('UncaughtException 😅');
console.log(err.name, err.message);
server.close(() => {
process.exit(1);
});
});Section 6
JSON Web Token
Cookies
速率限制 express-rate-limit
Http headers
XSS
param pollution
Section 7
Data Modeling
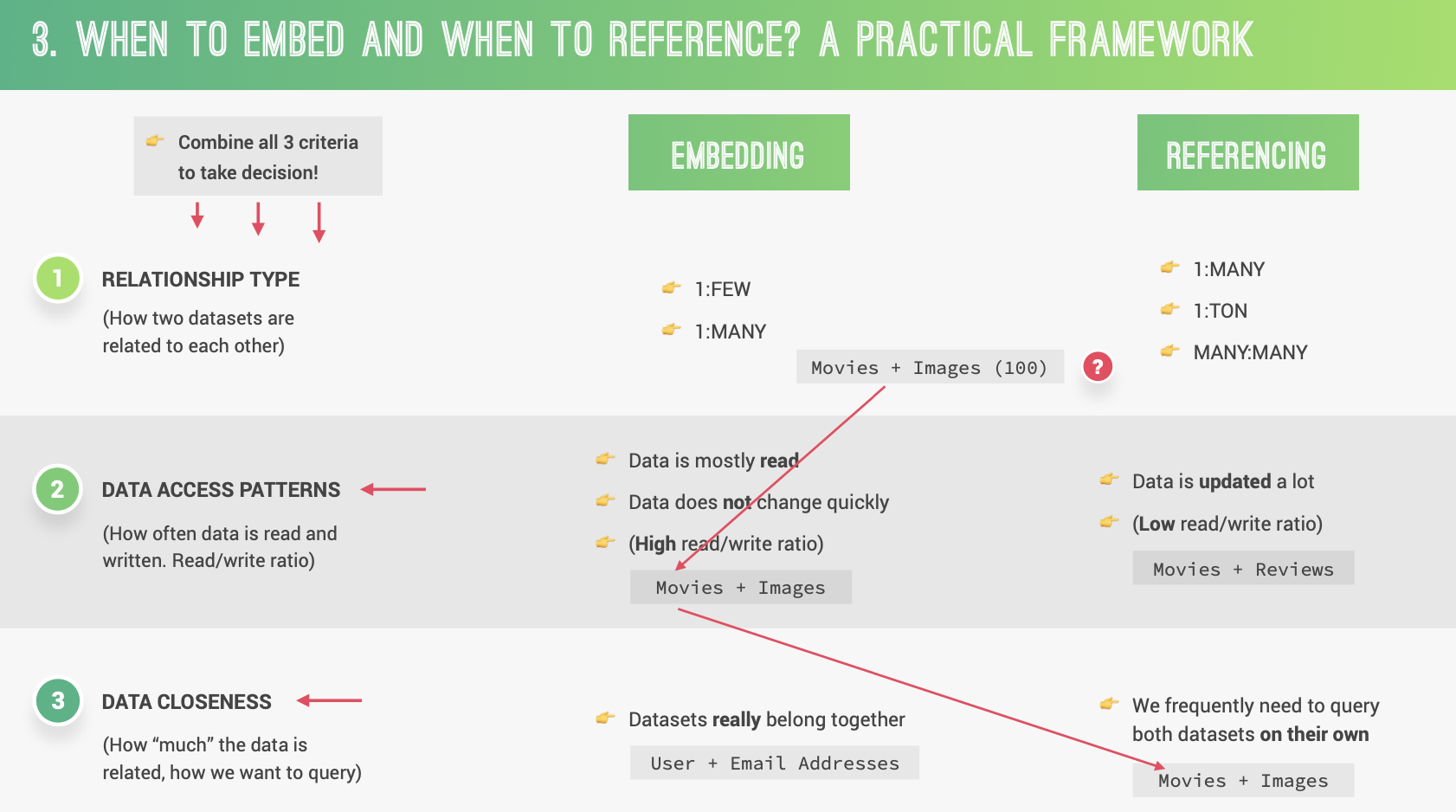
const userModel = Mongoose.**model**('User', userSchema);
注册名很重要,不然在其他 model 里 reference populate 的时候,会报没有注册的 bug。